Psychological Lab
The Psychological Posner Lab at the Faculty of Psychology analyzes the behavioral and neuropsychological mechanisms underlying psychological processes. To do this, it uses an advanced instrumentation that measures or influences psychological and neurological processes. In the Lab we take care of the organization and planning of experiments and the analysis of both behavioral and neuropsychological data.
The following instrumentation is currently available in the Lab:
- Stimulating the brain by means of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS)
- Measurement of eye movements
- Digital experiments on cognitive processes in 16 separate research cubicles using Eprime programming and others
- In-house tests developped for all sorts of measurements, including social brain and sleep
- Use and support of online experiments programmed in Eprime and Gorilla
- In-house scripts for analysis of neurological MRI data based for SPM analysis
The transition from the behavioral data (accuracy and reaction time), neurological imaging and neurostimulation to the psychological interpretation is a delicate and important step in making the best use of the laboratory instrumentation. The collected data is then analyzed and interpreted based on the current literature.
For all requests for collaboration and use of the instrumentation, please contact the head of the lab, Prof. Frank Van Overwalle, or the respective researchers indicated below.

LAB welcome room |

Lab hall with doors to cubicles for individual testing (with PC available) |

LAB room |

Lab hall with doors to cubicles for individual testing (with PC available) |
Transcranial direct current stimulation (Dr. Elien Heleven, Prof. Kris Baetens & Prof. Natacha Deroost)
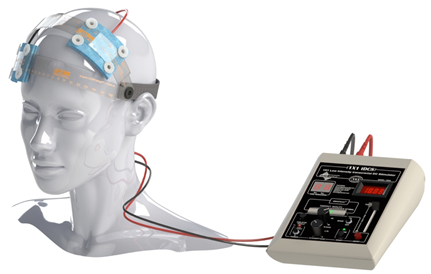
1X1 TDCS (LOW INTENSITY DIRECT CURRENT STIMULATOR)
Soterix Medical Inc, New York, USA
https://soterixmedical.com/research/1x1/tdcs
This “conventional” tDCS device is used to generate and deliver a low intensity current (usually 1-2 mA) through a pair of identical square rubber electrodes (one anode and one cathode), placed in rectangular saline-soaked sponges.
Anodal stimulation (i.e. with the excitatory, stimulating electrode positioned over the target area) generally leads to an excitation of the target area, whereas cathodal stimulation (i.e. with the inhibitory electrode positioned over the target area) exerts an inhibitory effect on the target area.
For the stimulation of the primary motor cortex (M1), for instance, the anodal (excitatory) electrode is placed over C3 or C4 according to the international 10-20 electroencephalogram system, matching with the left or right M1, respectively. Accordingly, the reference electrode can be positioned on the contralateral
supraorbital area.
4X1 HD-TDCS (MULTI-CHANNEL STIMULATION INTERFACE)
Soterix Medical Inc, New York, USA
https://soterixmedical.com/research/hd-tdcs
Recently, this “High Definition” (HD) tDCS device has been commercialized. By connecting the conventional tDCS device to this “adapter”, the direct current is delivered along the 4x1 HD-tDCS configuration. In contrast to the relatively large sponge-electrodes used in conventional tDCS montages, stimulation via HD-tDCS is delivered by means of one central gel-electrode and four return-electrodes placed in plastic encasings, embedded in an EEG cap.
By delivering the current through these smaller electrodes, neuromodulation is expected to be restricted to the desired area. In other words, a more specific, high-resolution stimulation of the target area is achieved.

|

|
| Adapted from https://soterixmedical.com/research |
Tests of social sequencing (cf. social cerebellum; Prof. Frank Van Overwalle)
| see link. |

|
Sleep and performance research (Prof. Olivier Mairesse)
HARDWARE
- Ambulatory Polysomnography (Somnoscreen, Alice PDX, etc.)
- Actigrafy/activity Trackers (FitBit/ActiWatch)
- Motor Performance Series (MLS)
- Carnetsoft Driving Simulator (in aanschaffing)
IN-HOUSE SOFTWARE
- Behavioral Sleep Resistance Task (BSRT)
- Psychomotor Vigilance Task (e-PVT)
IN-HOUSE QUESTIONNAIRES/SELF-REPORT SCALES
- Brugmann Fatigue Scale (BFS)
- Chronotype Questionnaire II (ChQ-II)
- Six Item Chronotyping (SIC)
- Visuo-Spatial Judgement Task for Sleepiness (VSJT-19)
- Sleep Screening Scale (SSS)